MyProtein - L-Carnitine Amino Acid
84.00₾
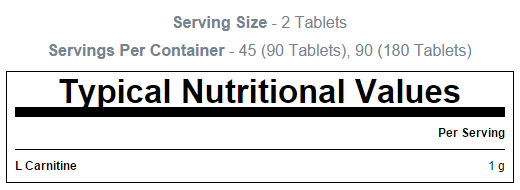
| Quantity | 180 pills |
|---|---|
| Portion/servings | 90 |
In stock
Out of stock
DESCRIPTION
General description
Enzymatic UV-Test with a linearity in the range of 5.6 - 112 μM L-carnitine in the test solution.
Application
Determination of L-carnitine in seminal plasma, serum, or urine in life science research applications.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-carnitine is an abundant amino acid present in red meat. Its trimethylamine structure has similarity to that of choline. The major source of this amino acid is by dietary ingestion. In mammals, it is also endogenously produced from lysine. It participates in the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondrial compartment. It produces trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) and promotes atherosclerosis.
Packaging
1 kit containing 6 components
Principle
L-Carnitine is acetylated to acetyl carnitine by acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) in the presence of the enzyme carnitine acetyl transferase (CAT). The resulting coenzyme A (CoA) is acetylated back to acetyl CoA in the presence of adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP) and acetate, catalyzed by the enzyme acetyl CoA synthetase (ACS). This results in the formation of adenosine-5′-monophosphate (AMP) and inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). In the presence of ATP, supported by myokinase (MK), AMP forms twice the amount of adenosine-5′-diphosphate (ADP). This is converted in the following reaction with phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) in the presence of pyruvate kinase (PK). The pyruvate formed is reduced to L-lactate by reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) in the presence of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). The amount of NADH consumed during the reaction is equivalent to half the amount of L-carnitine. NADH is measured spectroscopically at 340 nm.
Preparation Note
Storage conditions (working solution): Note:
- After reconstitution, the solution 1 is stable for 4 days at 2 to 8 °C.
- Bring solution 1 to 15 to 25 °C prior to use.
- After reconstitution, the suspension 2 is stable for 3 months at 2 to 8 °C.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Delivery service
Delivery throughout Tbilisi
- The cost of delivery service throughout Tbilisi is 4 GEL
- Delivery service is open from Monday to Friday from 11:00 to 20:00
- Delivery takes place within 2 working days after placing the order.
- You can use express order, which means delivery of the fixed order before 17:00 on the same working day, which costs 8 GEL.
- If the total cost of the order is 200 GEL or more, the delivery service is free.
- You can pay for the product either by using our bank card as a website, as well as by transferring money to the company's account or by receiving a parcel on the spot, both by plastic card and by cash. (You must indicate this information when placing an order)
Delivery throughout Georgia
When using delivery throughout Georgia, the cost of the product is paid only through an online bank account or by pre-transferring money to the company's account.
Georgian post
On the second working day after placing the order, the order is transferred to the Georgian Post, the average transportation time of which is 2-3 working days. To pick up the message, you must go to the relevant Georgian post office. You pay the shipping cost when receiving the parcel according to the weight of the shipment (average 8-15 GEL).








.webp)







მიმოხილვა
მიმოხილვები ჯერ არ არის.